
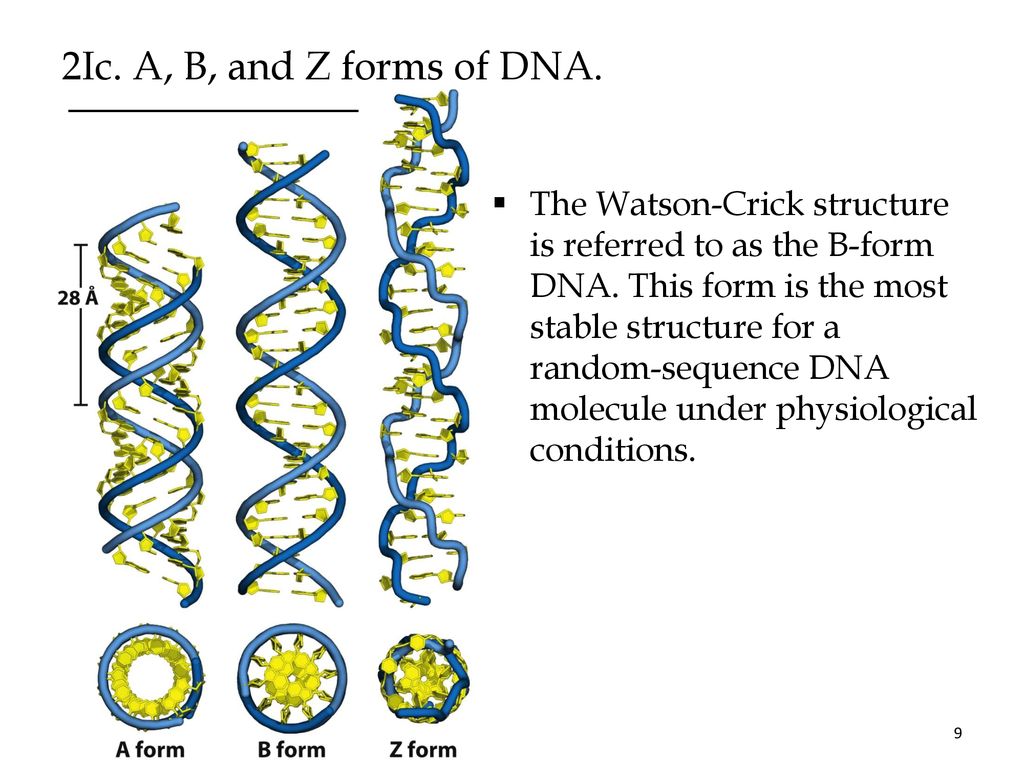
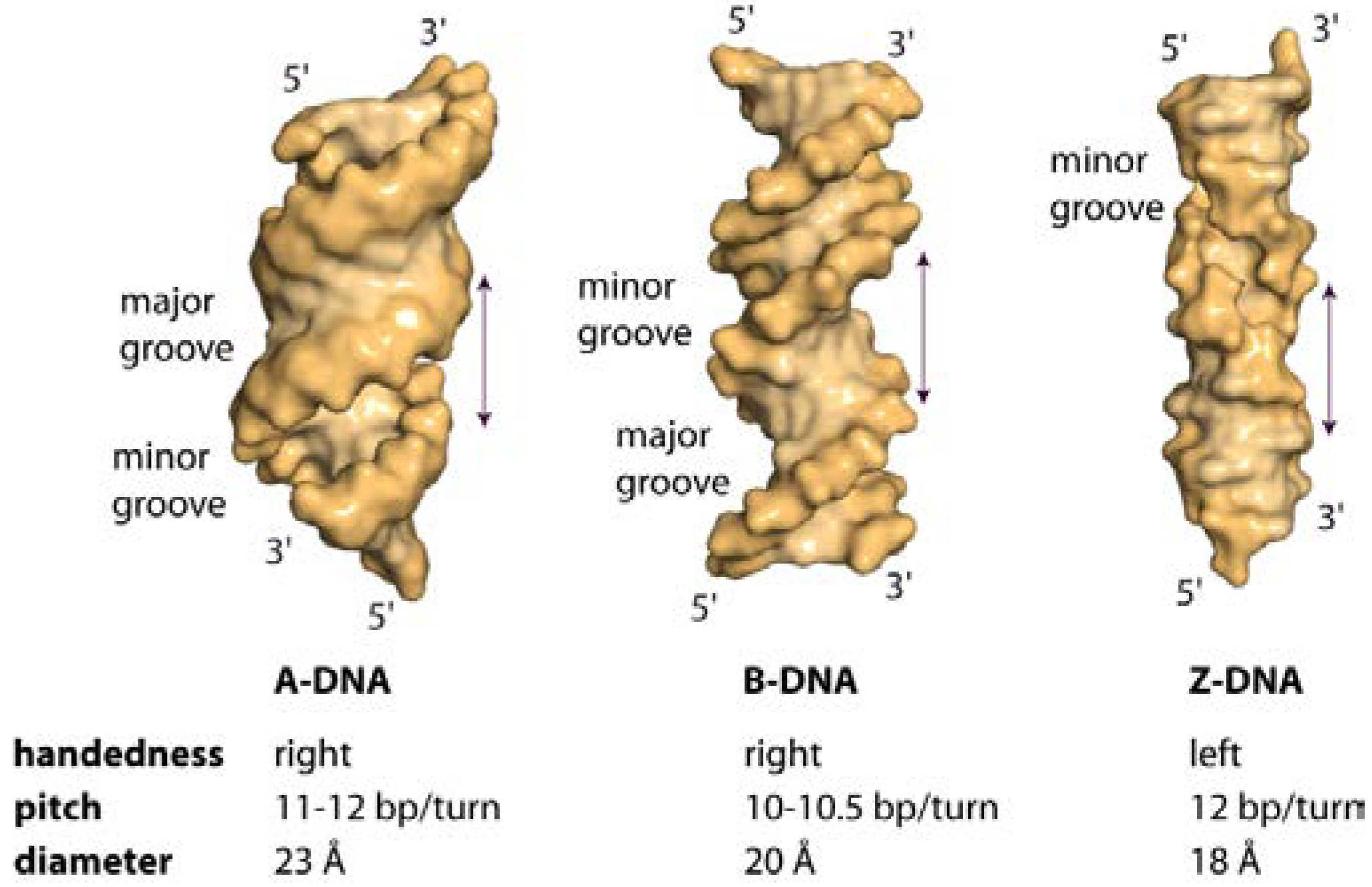
The major difference between A-form and B-form nucleic acid is in the confirmation of the deoxyribose sugar ring. 34° helix pitch -6° base-pair tilt 36° twist angle A-form DNA 9 nm (about 2.0 nm or 20 Angstroms) in diameter. 34 nm between bp, 3.4 nm per turn, about 10 bp per turn. The base‑pairing scheme immediately suggests a way to replicate and copy the genetic information. Two H‑bonds can form between A and T, and three can form between G and C. This pairs a keto base with an amino base, a purine with a pyrimidine. From Chargaff’s rules, the two strands will pair A with T and G with C. The nucleotides arrayed in a 5′ to 3′ orientation on one strand align with complementary nucleotides in the 3′ to 5′ orientation of the opposite strand.īases fit in the double helical model if pyrimidine on one strand is always paired with purine on the other.

The two strands of the duplex are antiparallel and plectonemically coiled. The two strands are held together by H‑bonding between the bases (in anti-conformation). They proposed two strands of DNA - each in a right‑hand helix - wound around the same axis. The Different Forms of DNA B-form DNAī-DNA is the Watson–Crick form of the double helix that most people are familiar with. The double helix is not the same uniform structure. For example, a 200-bp piece of DNA can run as if it were more than 1000 bp on an acrylamide gel if it has the right sequence. Refined resolution of the structure of DNA, based on X-ray crystallography of short synthetic pieces of DNA, has shown that there is considerable variance of the helical structure of DNA, based on the sequence. In nearly all cells, from simple bacteria through complex eukaryotes, the DNA must be compacted by more than a thousand-fold in order even to fit inside the cell or nucleus. There is simply not enough room for the DNA to be stretched out in a perfect, linear B-DNA conformation. The helical structure of DNA is thus variable and depends on the sequence as well as the environment. In addition to this classic structure, several other forms of DNA have been observed. The right-handed double-helical Watson – Crick Model for B-form DNA is the most commonly known DNA structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
